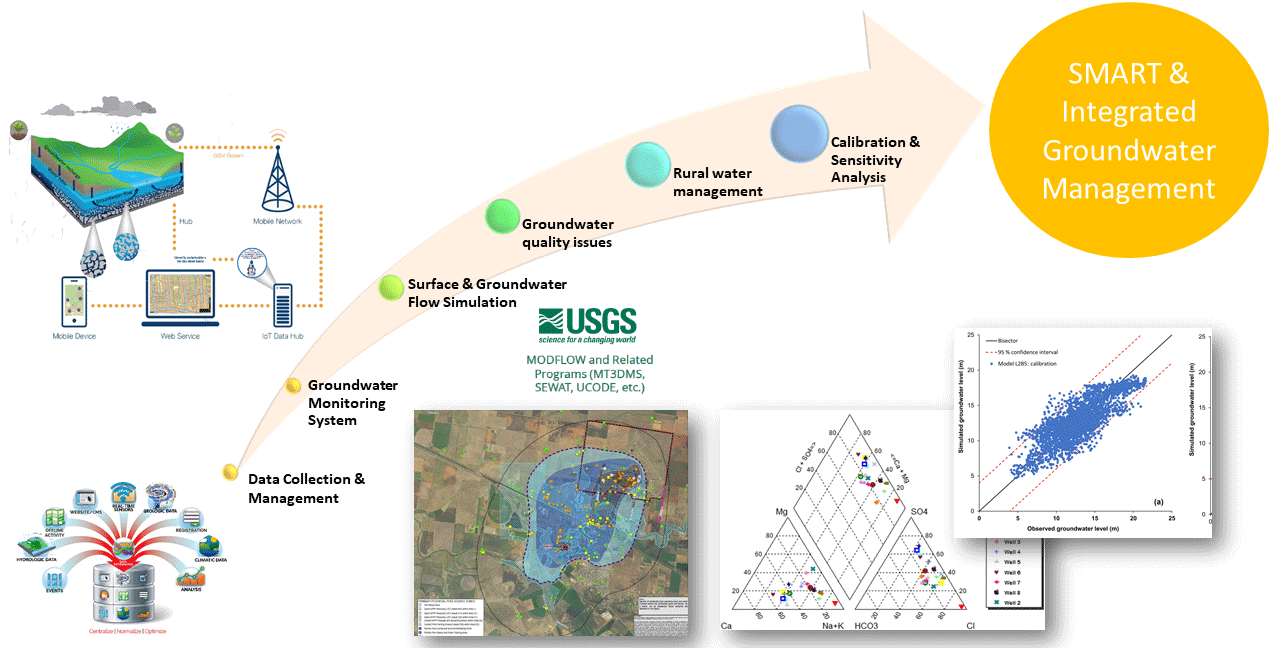
Effective management and protection of groundwater resources require detail knowledge and quantitative/qualitative characterization of aquifers. Thus, modeling and planning of the GW through the use of modern technologies and approaches have become of high priority towards this direction.
Moreover, the combined use of IoT and GIS is a valuable tool for the analysis of voluminous hydrogeologic data and for the simulation modeling of complex subsurface flow and transport processes under saturated and unsaturated conditions.
The concept of data fusion involves the merging of multiple data types to develop more reliable predictive models and to address basic and applied scientific questions concerning GW modeling.
The research team will use the FREEWAT (FREE and open source tools for WATer resource management) platform as a tool to the assessment of of water balances and the availability of water resources in space and time, in order to support the management and planning processes in the aquifer of the Lower Valley of Medjerda.
Indeed, The FREEWAT platform integrates a hydrological model in the QGIS GIS interface, where data are managed through a Spatial Data Base Management System (DBMS), and two versions of MODFLOW, a physically-based, spatially distributed code, which simulates the groundwater flow dynamics using a 3D block-centered finite-difference approach, in which the spatial domain is discretized in rectangular or square cells. Flow associated with external stresses, such as wells, areal recharge, evapotranspiration, drains, rivers, and lakes can be simulated as well.